| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 웹 기술면접
- 괄호의값 스택
- 개발일지
- 유니온 파인드
- Spring Security
- 커머스기사
- 프로그래머스
- 자바 2869
- 자바 1193
- 다익스트라 최소비용구하기
- 데이터베이스 기초지식
- 2504 괄호의값 자바
- 줄세우기 위상정렬
- 기업분석
- Union Find
- 백준 괄호의값 자바
- 백준 1700 자바
- 조인종류
- 백준 2252 자바
- 백준 최소비용구하기 자바
- 백준 1193
- 백준 멀티탭스케줄링 자바
- 백준 줄세우기 자바
- 라이브커머스
- 이커머스
- 1062번 가르침
- 인사관리사이트
- 온라인쇼핑
- 백준 1806 자바
- 팀프로젝트
- Today
- Total
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 웹 기술면접
- 괄호의값 스택
- 개발일지
- 유니온 파인드
- Spring Security
- 커머스기사
- 프로그래머스
- 자바 2869
- 자바 1193
- 다익스트라 최소비용구하기
- 데이터베이스 기초지식
- 2504 괄호의값 자바
- 줄세우기 위상정렬
- 기업분석
- Union Find
- 백준 괄호의값 자바
- 백준 1700 자바
- 조인종류
- 백준 2252 자바
- 백준 최소비용구하기 자바
- 백준 1193
- 백준 멀티탭스케줄링 자바
- 백준 줄세우기 자바
- 라이브커머스
- 이커머스
- 1062번 가르침
- 인사관리사이트
- 온라인쇼핑
- 백준 1806 자바
- 팀프로젝트
- Today
- Total
JumpUp
백준 [N1916 - 최소비용구하기]_Dijkstra 본문

해당 문제에서는 다익스트라 알고리즘이 활용됩니다.
다익스트라는 하나의 노드에서 다른 모든 노드로 가는 최단 경로를 탐색하는 알고리즘입니다.
양의 가중치만 존재할 때 이 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있습니다.(이 점이 DFS, BFS을 활용한 최단경로 구하기와 다른 점 입니다.) 음의 가중치가 하나라도 있으며 다익스트라를 사용할 수 없다는 특징이 있습니다.
풀이과정
필요한 자료구조는 크게 4가지입니다.
통행정보 저장할 가중치 인접리스트 ArrayList<Bus>[] arr,
도시 방문여부 확인할 visited배열,
최소비용갱신할 dis배열,
현재노드와 연결된 간선정보를 저장할 우선순위큐
1. 노드와 가중치를 담은 Bus 클래스를 선언합니다.
가중치를 기준으로 정렬할 수 있도록 compareTo를 Override해줍니다.
2. dis배열을 무한대(int의 최대값)로 초기화합니다. 방문배열 visited와 가중치 인접리스트 arr를 선언 및 초기화합니다.
3. 우선순위큐를 선언하고 우선순위큐에 시작노드 객체를 추가하고 dis[시작노드] = 0으로 셋팅해줍니다.
4. 우선순위큐가 빌 동안 모든 노드를 탐색합니다.
4-1. 현재노드(bus.end)와 연결된 next(간선정보) 중 next.end가 방문하지 않았고,
dis[next.end] > dis[bus.end] + next.cost이면 //현재노드를 거쳐가는 것이 더 최소비용일 경우 dis배열을 갱신
dis[next.end] = dis[bus.end] + next.cost로 갱신합니다.
4-2. 우선순위큐에 next노드 객체를 add합니다.
4번의 과정들을 간단한 예시로 제대로 이해했는지 짚어보겠습니다.
1부터 3까지 가는 최소 비용구하기.
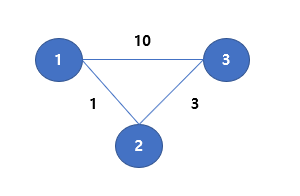
STEP1. 현재노드 1, next노드 2
dis배열
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 0 | 1 | ∞ |
우선순위큐(end, cost)
(2,1)
STEP2. 현재노드 1, next노드 3
dis배열
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 0 | 1 | 10 |
우선순위큐(end, cost)
(2,1), (3,10)
STEP3. 현재노드 2, next노드 3
dis배열
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 0 | 1 | 4 |
우선순위큐(end, cost)//가중치 기준으로 오름차순 정렬됨
(3,4), (3,10)
STEP4. 현재노드 3인데, 3과 연결된 모든 노드가 방문되었기 때문에 종료되고 dis[3] = 4가 반환된다.
전체코드
public class Main{
private static int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static ArrayList<Bus>[] arr;
private static boolean[] visited;
private static int[] dis;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int M = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
StringTokenizer st;
arr = new ArrayList[N+1];
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
arr[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
visited = new boolean[N+1];
dis = new int[N+1];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int cost = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr[start].add(new Bus(end, cost));
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
System.out.println(dijkstra(start, end));
br.close();
}
public static int dijkstra(int start, int end){
PriorityQueue<Bus> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Bus(start, 0));
dis[start] = 0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Bus bus = pq.poll();
if(!visited[bus.end]){
visited[bus.end] = true;
for(Bus next : arr[bus.end]){
if(!visited[next.end] && dis[next.end]>dis[bus.end]+next.cost){
dis[next.end] = dis[bus.end]+next.cost;
pq.add(new Bus(next.end, dis[next.end]));
}
}
}
}
return dis[end];
}
public static class Bus implements Comparable<Bus> {
private int end;
private int cost;
public Bus(int end, int cost){
this.end = end;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Bus o) {
return this.cost - o.cost;
}
}
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 단계별로풀어보기 [문자열] 복습 (0) | 2022.10.22 |
|---|---|
| 백준 [N2252 - 줄 세우기]_위상정렬(Topological Sort) (0) | 2022.03.02 |
| 백준 [N1806 - 부분합] (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| 백준 [N1700 - 멀티탭스케줄링] (0) | 2021.12.27 |
| 백준 [N1062 - 가르침] (0) | 2021.12.21 |